Dr S Aishwariya discusses the difference in philosophy, approach and perception
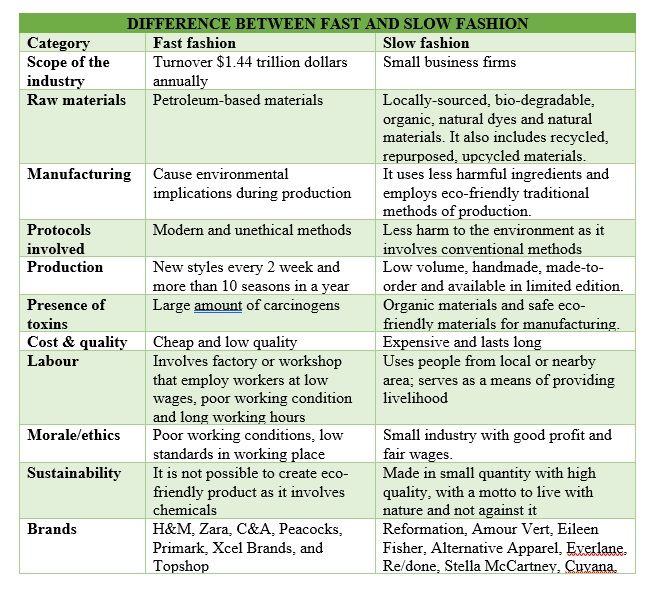
Fast fashion denotes lower-quality, low-priced, mass-produced and machine-made garments that quickly end up in landfills. Slow fashion garments in contrast are made by hand, consume time to produce, use artistic talent, have better quality and are priced higher. Slow fashion garments are naturally warm and comfortable over a period of washes. These can last for years or even a lifetime. Sustainable fashion is concerned with use of fibres from organic, recycled, repurposed and upcycled materials. The selection is made by opting for materials with less chemicals, dyes, energy, less resource, less waste and minimal impact.
Slow fashion

Kate Fletcher, author of Sustainable Fashion and Textiles, has explained the urge to shift to a more sustainable fashion industry. The word was coined by her following the slow food movement that was a huge hit in the food industry. The main characteristic of slow fashion is that it is not produced in bulk. It is also done with emphasis on skills of the craftsman. The raw materials are sourced locally and as the product is handcrafted and quality checked at every step, it makes the product expensive.
Slow fashion is ethical and serves as a bond between raw materials, labour force and environment. The classic designs and traditional methods of making a fabric and clothing is part of it. Slow fashion is not seasonal. It does not work like a trend. But takes time in preparation and production, and has a purpose with intention. This holistic approach considers the complete life cycle of the product. The products in slow fashion are not disposable. These are sustainable and targeted to serve a long period. These are often available in small stores and not in large retail outlets and have limited collections every year.
People have a choice to buy things that are of better quality, mostly natural, organic, limited edition and bio-degradable. It is a result of awareness caused by the harmful effects of fast fashion. The focal point of slow fashion is sustainability. The benefits are good quality products with clean environment and fair policies for consumers and producers. The slow fashion concept puts emphasis on quality over quantity. Carbon footprints are higher in fast fashion. Quality and longevity, fair wages and zero waste encourages slow production. It takes time to ensure quality, value to production, and connection with the environment. Fair labour, satisfying human needs, supporting local business, eco-friendly supply chain, true retail price, resourcefulness, clean and efficient production and sustainable protocols in product development are the target of show fashion.
Ethical fashion is a popular term in slow fashion. This is associated with animal and human rights. Working conditions, fair wages, child labour, animal testing are some of the parameters considered in ethical fashion. Eco-fashion is another commonly associated concept.
Process of slow fashion

It begins with designing, which is done keeping in mind concerns regarding sustainability and ecology, and raw materials are sourced based on that. The second step is the production process, where quality of labour, fair wages and quality of life, awareness of quality, insisting on recycling and reuse are the key. Slow fashion is expressed as a philosophy through which a consumer is questioned on how he buys, wears and cares for his clothes. It is not a trend but based on environmental and ethical concerns. The procedures are transparent and the consumers come to know who made the clothes, how it is priced, and whether the labour was paid fair wages. Such products give a sense of belongingness to consumers. A soul inside the fabric can be felt which is the energy, love and craftmanship of the worker. Slow fashion usually involves three thoughtful steps,
• Design: Sustainable sources, ecological and ethical practice
• Production: Quality and craftmanship
-
Consumption: Longevity, sustainable investment
Some slow fashion brands
• & Other Stories: Works on instore recycling; a 10 per cent discount voucher is given to the customer when he gives a used cloth or empty beauty container.
• Reformation: The Refscale methodology developed by this US brand shows the amount of waste saved by buying the company's product.
• Everlane: This produces quality products that last for a lifetime. It transparently tells the consumer about every aspect of production. Good factory, happy labour and quality are the three dimensions at Everlane.
• Los Angeles Apparel: In addition to using local workers and paying decent wages, it makes garments from organic and recycled cotton.
• Matt & Nat: It manufactures handbags and belts. The interlining is given by recycled bottles. One bag uses 21 bottles. Rubber and cork are also used.
• People Trees: Uses natural fibres, bio-degradable materials and local craftsmanship, its products' USP is the artisans' skill.
• Cariuma: It uses canvas, raw rubber, leather to create sneakers.
References
1.https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/retail/our%20insights/measuring%20the%20fashion%20world/
measuring-the-fashion-world-full-report.ashx
2.https://www.sustainyourstyle.org/old-environmental-impacts
3.https://thegreenhubonline.com/2018/01/16/20-facts-about-the-fast-fashion-industry-that-will-shock-you/
4.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fast_fashion
5.https://dbknews.com/2019/08/13/fast-fashion-sustainability-recycling-employee-care/
6.https://www.bbc.com/news/newsbeat-47292087
7.https://www.coursehero.com/file/39011757/Zarappt/
8.https://goodonyou.eco/what-is-fast-fashion/
9.http://study-ny.com/slow-fashion
10.https://www.trustedclothes.com/blog/2016/05/17/slow-fashion-vs-fast-fashion/
11.https://www.channelone.com/interact_post/infographic-the-fast-facts-on-fast-fashion/
12.http://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2019/633143/EPRS_BRI(2019)633143_EN.pdf
13.https://www.fastcompany.com/3055925/5-new-solutions-for-the-fashion-industrys-sustainability-problem











Comments